Cooling towers are essential equipment used for heat rejection in industrial processes by transferring heat from water to the atmosphere. They are critical in maintaining optimal operational temperatures for industrial equipment. Cooling towers find applications across industries such as power generation, chemical processing, HVAC, and manufacturing. This guide covers various types of cooling towers conforming to ISO 10628-2 standards.
Cooling towers are represented in P&IDs with specific symbols indicating their design and functionality:
| Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
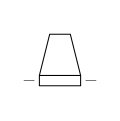 | Cooling Tower | General-purpose cooling tower for heat rejection. |
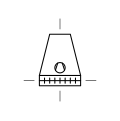 | Cooling Tower Dry with Forced Draught | Cooling tower that utilizes fans to force air over dry surfaces for cooling. |
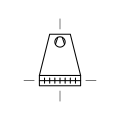 | Cooling Tower Dry with Induced Draught | Cooling tower that features fans that draw air over dry surfaces for cooling. |
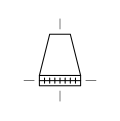 | Cooling Tower Dry with Natural Draught | Cooling tower that relies on natural convection for cooling without mechanical fans. |
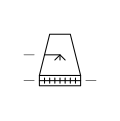 | Cooling Tower Wet-Dry with Natural Draught | Cooling tower that combines wet and dry cooling mechanisms with natural draught. |
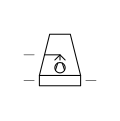 | Cooling Tower Wet with Forced Draught | Cooling tower that employs fans to force air through wet surfaces for enhanced cooling. |
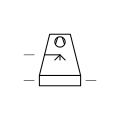 | Cooling Tower Wet with Induced Draught | Cooling tower that draws air through wet surfaces for efficient cooling. |
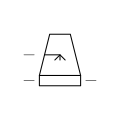 | Cooling Tower Wet with Natural Draught | Cooling tower that uses natural convection for cooling water over wet surfaces. |
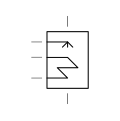 | Spray Cooler | Cooling tower that uses spray nozzles to distribute water and enhance cooling efficiency. |
Cooling towers are used in various applications requiring heat rejection and temperature regulation, including:
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Equipment Type | Cooling Tower |
| Design | Dry, Wet, Natural Draught, Forced Draught |
| Operation | Heat Rejection via Water-Air Exchange |
| Standards | ISO 10628-2, ASME |
| Industries | Power Generation, HVAC, Chemicals |
| Component | Material Options |
|---|---|
| Casing | FRP, Galvanized Steel, Stainless Steel |
| Fill | PVC, Polypropylene |
| Fans | Aluminum, Composite |
| Piping | Stainless Steel, PVC |
| Attribute | Options |
|---|---|
| Capacity Range | 10 m³/h to 100,000 m³/h |
| Temperature Drop | 5°C to 15°C |
| Fan Speed | 500 to 2,000 RPM |
| Air Flow Rate | 5,000 to 200,000 m³/h |
| Noise Level | Below 85 dB(A) |
| Accessory | Details |
|---|---|
| Drift Eliminators | Reduces water loss through drift |
| Spray Nozzles | Ensures uniform water distribution |
| Fan Stack | Enhances air movement efficiency |
| Control Panel | Automates fan and water flow control |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Material | FRP |
| Type | Wet with Induced Draught |
| Capacity | 50,000 m³/h |
| Air Flow Rate | 100,000 m³/h |
| Application | Industrial Cooling |
Explore micro data sheets for cooling towers using mD.
Explore vendors for cooling towers in your region using Mails AI.
| Parameter | Specification | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized Steel | $10,000 - $100,000 |
| Type | Wet with Forced Draught | $20,000 - $200,000 |
| Capacity | 50,000 m³/h | $50,000 - $500,000 |
For accurate pricing of cooling towers, access cost data using Cost AI.
To integrate this 3D model of a cooling tower in a Process Plant use Model Builder. Download cooling-tower.json. Choose File > Import and use the downloaded file to add the model to the scene. Choose Add > Light > Directional to add directional light.
Cooling towers are indispensable for efficient heat rejection in industrial processes. Their diverse designs and operational capabilities make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Use this guide alongside tools like mD (Micro Data Sheets), Vendor Lists, and Cost AI to make informed decisions and optimize your processes.