Compressors are essential mechanical devices designed to increase the pressure of gases or create a vacuum by reducing their volume. Widely used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals, compressors play a crucial role in enabling processes like refrigeration, gas transfer, and vacuum creation. This guide covers various types of compressors conforming to ISO 10628-2 standards.
Compressors are represented in P&IDs with distinct symbols that highlight their operational principles and configurations:
| Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
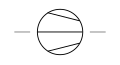 | Compressor Centrifugal Type | A mechanical device that uses a high-speed impeller to compress gases. |
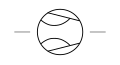 | Compressor Ejector Type (Vacuum Pump Jet) | A mechanical device that operates by creating a vacuum using high-velocity jet streams. |
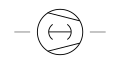 | Compressor Rotary Type (Vacuum Pump Rotary Piston Type) | A mechanical device that utilizes a rotating piston mechanism to compress gases or create a vacuum. |
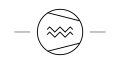 | Compressor Screw Type | A mechanical device that features intermeshing screws to compress gases. |
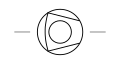 | Compressor Vacuum Pump Diaphragm Type | A mechanical device that employs a flexible diaphragm to compress gases or create a vacuum. |
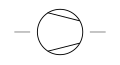 | Compressor Vacuum Pump | A general-purpose vacuum pump for diverse industrial applications. |
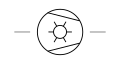 | Compressor Vacuum Pump Liquid Ring Type | A mechanical device that uses a liquid ring to compress gases and create a vacuum. |
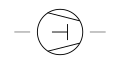 | Compressor Vacuum Pump Reciprocating Piston Type | A mechanical device that uses a piston-cylinder mechanism to create a vacuum. |
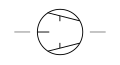 | Compressor Vacuum Pump Roller Vane Type | A mechanical device that employs a rolling vane mechanism for gas compression and vacuum generation. |
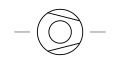 | Compressor Vacuum Pump Turbo Type | A mechanical device that uses high-speed rotating blades to generate a vacuum. |
Compressors are used in a variety of applications requiring gas compression or vacuum generation, including:
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Equipment Type | Compressor |
| Design | Centrifugal, Screw, Piston, Rotary, Liquid Ring |
| Operation | Gas Compression, Vacuum Creation |
| Standards | ISO 10628-2, ASME |
| Industries | Oil and Gas, Pharmaceuticals, Food and Beverage |
| Component | Material Options |
|---|---|
| Casing | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel |
| Rotor/Impeller | Stainless Steel, Aluminum |
| Seals | PTFE, Graphite |
| Bearings | High-Speed, Ceramic |
| Attribute | Options |
|---|---|
| Capacity Range | 10 m³/h to 10,000 m³/h |
| Pressure Range | 0.1 bar to 500 bar |
| Speed Range | 500 to 50,000 RPM |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to 200°C |
| Accessory | Details |
|---|---|
| Control Panel | For automated operation |
| Vibration Monitoring System | Ensures operational safety |
| Cooling System | Air or water-cooled systems |
| Silencers | Reduces noise during operation |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Material | Stainless Steel |
| Type | Screw Type |
| Capacity | 5,000 m³/h |
| Pressure Rating | 200 bar |
| Application | Gas Compression |
Explore micro data sheets for compressors using mD.
Explore vendors for compressors in your region using Mails AI.
| Parameter | Specification | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Carbon Steel | $10,000 - $100,000 |
| Type | Screw Type | $30,000 - $150,000 |
| Capacity | 5,000 m³/h | $50,000 - $200,000 |
For accurate pricing of compressors, access cost data using Cost AI.
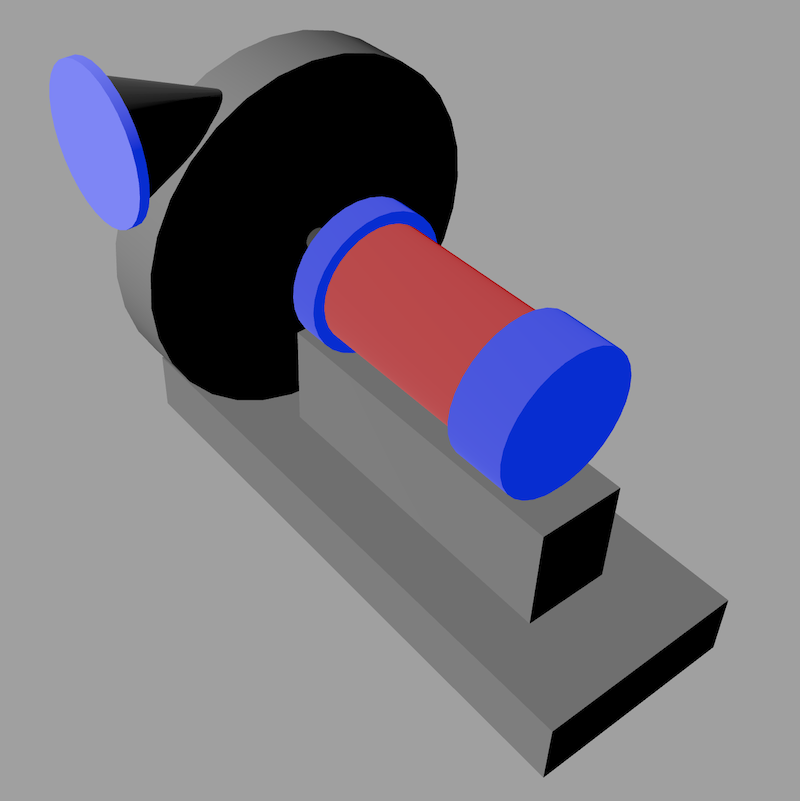
To integrate this 3D model of a compressor in a Process Plant use Model Builder. Download compressor.json. Choose File > Import and use the downloaded file to add the model to the scene. Choose Add > Light > Directional to add directional light.
Compressors are critical for enabling efficient gas compression and vacuum creation in industrial processes. Their diverse designs and operational capabilities make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Use this guide alongside tools like mD (Micro Data Sheets), Vendor Lists, and Cost AI to make informed decisions and optimize your processes.